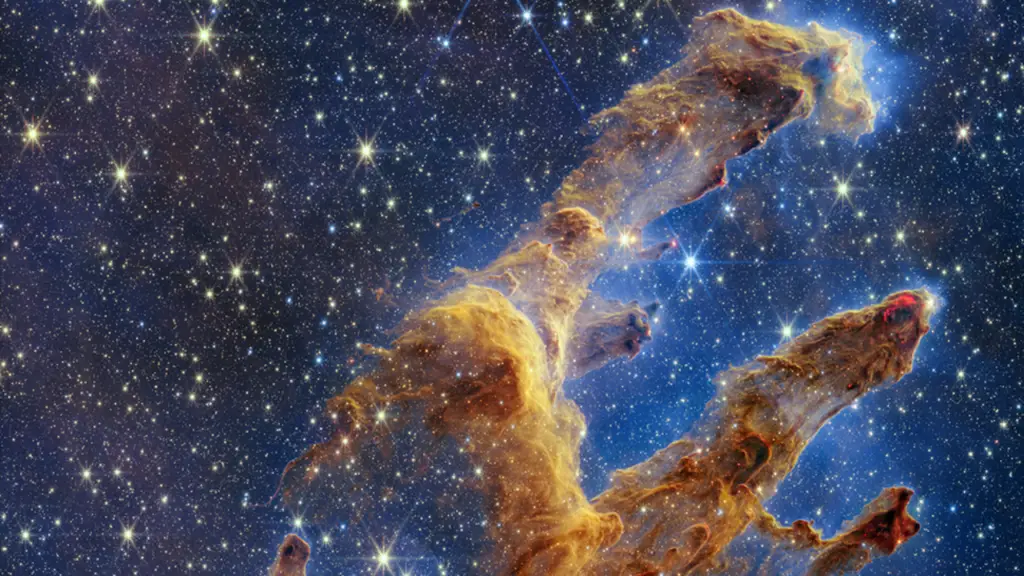
On October 19th, 2022, NASA officially released a new image of the Pillar of Creation recently captured by NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope. The next-generation space telescope used its Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam) to capture the pillar of Creation in a highly detailed landscape. The infrared image of the Webb Space Telescope shows where new stars are forming within the interstellar dense clouds of gas and dust.
Unlike the Hubble, James Webb revealed a more detailed view of the three-dimensional pillars that appears like fascinating rock formations. Even though the pillars are made up of dust and gas, they appear to be semi-transparent in near-infrared light. Despite the view of the Pillar of Creation first made popular by the Hubble Space Telescope in 1995, Webb’s image of the object reveals a more detailed outlook.
What is the Pillar of Creation?
The Pillar of Creation is one of the most fascinating nebulae that have Captured our astronomical interest for decades. After Swiss astronomer Jean-Philippe Loys de Chéseaux discovered the Pillar of Creation in 1745, scientists around the globe have been curious to learn more about this nebula. The Pillar of Creation was discovered as an elephant trunk of interstellar gas and dust in the Eagle Nebula. It is located in the Serpens constellation which is about 6,500–7,000 light-years from Earth. They were named the Pillar of Creation as the gas and dust are always in the process of creating new stars while being disrupted by the light emanating from nearby stars that were newly born.
Explaining the New Image of Pillar of Creation as Captured by the James Webb Space Telescope

Credits: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI; Joseph DePasquale (STScI), Anton M. Koekemoer (STScI), Alyssa Pagan (STScI).
This new infrared image of the Pillar of Creation as captured by the Webb Telescope reveals the object in extremely high definition. Looking closely at the image, you will see a glowing bright red wavy line at the edges of some pillars. These lines show where stars are ejecting materials as they form. The bright red orbs seen in the image are newly created stars that are adding a unique beauty to the pillars.
These orbs basically have diffraction spikes and they stay outside one of the dusty pillars. Unlike past Webb images where distanced galaxies do appear in the background, this fascinating image only reveals only layers of gas and dust that are drawn like a curtain to enable stars to occur at the center stage.
Conclusion
Scientists will surely leverage these Webb images to update their models of star formation. Future discoveries will enable us to learn how stars are created and bust out of these dense interstellar clouds of gas and dust. What do you think about this fascinating discovery?